The following are some articles/white papers that I wrote to improve communication and understanding of ideas (especially AI-related):
A Comprehensive Review of AI Myths and Misconceptions (2023)

Giving people realistic expectations and AI literacy can improve discussions about the benefits and costs of AI technology, how and when it should be used, and what we want our future with AI to look like. Myths and misconceptions about AI can impede these debates and, at worst, cause bad actions or decisions. To avoid this, this review clarifies common myths and misconceptions about AI through simple explanations and remarks. The review is written for a broad audience because a realistic understanding of artificial intelligence (AI) technology benefits everyone.
[Paper] [Paper – short version (LinkedIn Post)] Note: AI-generated image.
Plan, Pitch, Perform: From Data Science Idea to Funded Project (2025)
Do you have a data science idea in mind? Great! But how do you turn it into a project and set it up for success? Many data science projects never make it to production, not just due to technical issues, but because they lack a connection to real business and end-user needs. This practical guide shows how to avoid such pitfalls. PLAN: Use the practical checklists in this guide to ask the right questions, conduct targeted research, and carry out low-cost experiments. PITCH: Win support by crafting and presenting a strong project proposal. PERFORM: Execute the project!
[Paper]
SUCCESSFUL COMMUNICATION OF COMPLEX INFORMATION (2023)

Complex information must be conveyed accurately and clearly. This requires both mastery of the subject and practical communication skills. This 12-page guide aims to improve the latter. It is primarily written for technical experts (e.g., data scientists) who need to communicate their findings to diverse stakeholders in business. However, the best practices and strategies in this guide are applicable beyond this scenario. Good communication has many universal benefits, including improved relationships. I hope you enjoy!
[Paper]
Selected peer-reviewed publications
Structuring Uncertainty for Fine-Grained Sampling in Stochastic Segmentation Networks
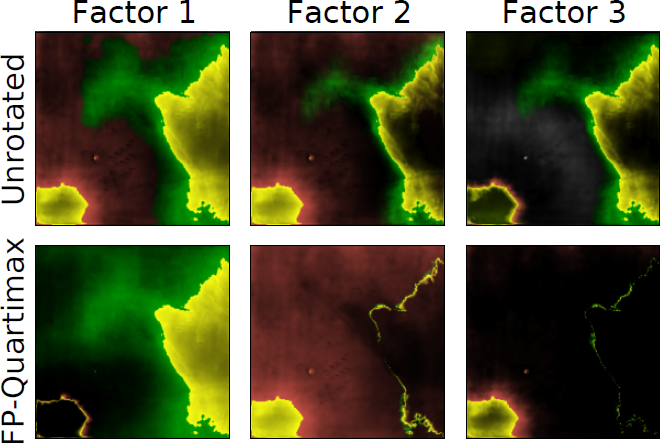
In this work, we explore Stochastic Segmentation Networks for image segmentation (a deep learning architecture). These networks predict segmentation uncertainty, which we structure into meaningful components, as seen in the bottom row of the image. This adds a layer of explainability of the AI output to humans. Through our user interface, humans can remix the contributions of individual components and thereby adjust the overall segmentation in a controlled manner.
Leveraging the Wikipedia Graph for Evaluating Word Embeddings
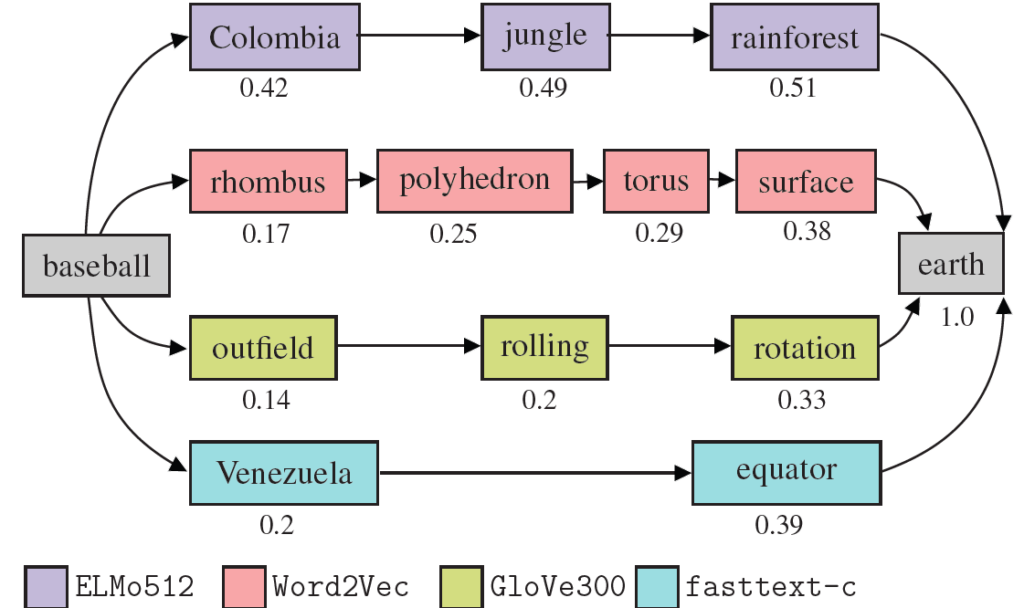
Deep learning for natural language processing (NLP) often relies on pre-trained word embeddings, that is, vector representations of words. A typical evaluation of these embeddings checks how well they capture word similarities. In this work, we measure similarity by routing the Wikipedia hyperlink graph, which encodes word similarities as edges between articles. Our approach not only avoids the costly human creation of similarity data sets, but also extends to other languages available at Wikipedia.
Robust principal component analysis for generalized multi-view models
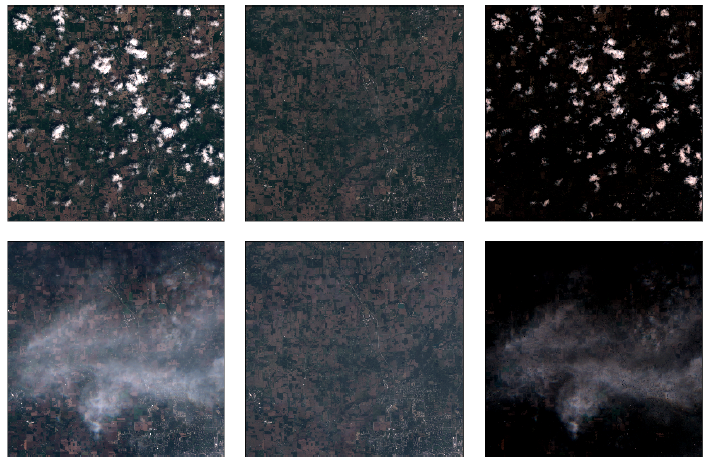
Principal component analysis (PCA) is susceptible to data corruption. A more robust approach decomposes a data matrix into (1) a low-rank component for the principal components, e.g., stable background, and (2) a sparse component for the data corruption, e.g., clouds as a moving foreground. This paper shows that for grouped measurements (e.g., multi-channel pixels), the decomposition can be recovered exactly when only the corrupted data matrix is given.